Blind protein structure predictions from CASP3 and CASP4
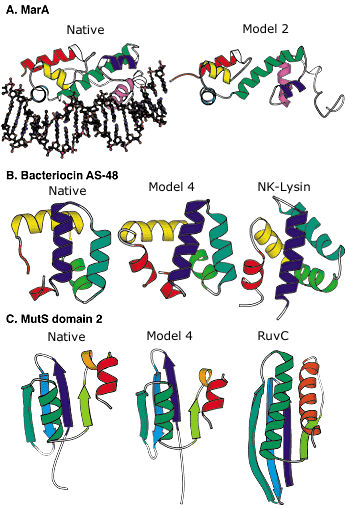 Blind protein structure predictions from CASP3 and CASP4. A: Left, crystal structure of the MarA transcription factor bound to DNA; right, our best submitted model in CASP3. Despite many incorrect details, the overall fold is predicted with sufficient accuracy to allow insights into the mode of DNA binding. B: Left, the crystal structure of bacteriocin AS-48; middle, our best submitted model in CASP4; right, a structurally and functionally related protein (NK-lysin) identified using this model in a structure-based search of the Protein Data Bank (PDB). The structural and functional similarity is not recognizable using sequence comparison methods (the identity between the two sequences is only 5 percent). C: Left, crystal structure of the second domain of MutS; middle, our best submitted model for this domain in CASP4; right, a structurally related protein (RuvC) with a related function recognized using the model in a structure-based search of the PDB. The similarity was not recognized using sequence comparison or fold recognition methods. Image: Rich Bonneau |

©2026 University of Washington
https://www.bakerlab.org